The main drone type most people fly is a quadcopter. A quadcopter gets its name from having four propellers, or rotors, as they’re also called.

Quadcopters can be recognized by their four propellers, or rotors
But quadcopters are just one type of drone. And categorizing drone types based on their number of propellers is just one way to organize drones.
[What is a 360 drone? Find out in our new guide.]
Here are the three ways drones are typically categorized:
- Rotor configuration. From multi-rotors to fixed wings and beyond, this category organizes drones based on the number of propellers they have, and how they’re configured.
- Size. From nano drones small enough to fit in your hand to large industrial drones built for heavy lifting and extended missions, this category organizes drones based on how big they are and what their size allows them to do.
- Use case. From drones made to shoot high-end movies to drones made just for inspectors, this category organizes drones based on the types of work they’re made to do.
Looking for specific information on drone types? Here’s a menu of everything we cover in this guide:
- Drone Types Overview
- Drone Types with Pictures
- Drone Type 1: Organized by Rotor Configuration
- Drone Type 2: Organized by Size
- Drone Type 3: Organized by Use Case
- New Drone Types—Emerging Drone Technologies
- Drone Types FAQ
Drone Types Overview
To kick things off, we want to give you an overview of the three different ways to categorize drones that we covered above.
Each section in the chart below includes examples of drones, their typical applications, and key features to help you choose the right one.
| Category | Drone Type | Examples | Typical Uses | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotor Configuration | Multi-Rotor Drones | DJI Mavic 3, DJI Matrice 30, Skydio 2+ | Photography, inspections, recreational flying | Stable hovering, precise controls, versatile use |
| Fixed-Wing Drones | WingtraOne, senseFly eBee X, Parrot Disco-Pro | Mapping, surveying, environmental monitoring | Long flight times, efficient energy usage, large area coverage | |
| Single-Rotor Helicopter Drones | Yamaha RMAX, Draganfly Commander 2 | Heavy payload transport, agriculture, research | High payload capacity, longer flight times | |
| Fixed-Wing Hybrid VTOL Drones | Quantum Systems Vector, DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise, WingtraOne VTOL | Surveying, search and rescue, industrial inspections | Vertical takeoff/landing, long-range flight, versatility | |
| Size | Nano Drones | Ryze Tello, SkyEye Nano | Indoor flying, casual use, beginner training | Lightweight, short flight times, affordable |
| Small Drones | DJI Mini 3 Pro, Autel EVO Nano+ | Travel, recreational flying, light photography | Portable, GPS stabilization, cameras up to 4K | |
| Medium Drones | DJI Mavic 3, Autel EVO Lite+, Sony Airpeak S1 | Professional photography, inspections, mapping | Advanced flight modes, obstacle avoidance, high-resolution cameras | |
| Large Drones | DJI Agras T40, DJI Matrice 300 RTK | Industrial inspections, agriculture, delivery | High payload capacity, rugged design, long flight times | |
| Heavy-Lift Drones | DJI Flycart 30, Freefly Alta X | Heavy payload transport, filmmaking | Reinforced frames, advanced stabilization, high weight capacity | |
| Use Case | Agriculture Drones | DJI Agras T40, senseFly eBee Ag, Parrot Bluegrass | Crop monitoring, soil analysis, pesticide spraying | Multispectral sensors, spraying systems, precision mapping |
| Delivery Drones | Flytrex Delivery Drone, Amazon Prime Air, DJI Flycart 30 | Medical supply transport, e-commerce logistics | Secure payload systems, autonomous navigation, long-range flight | |
| Inspection Drones | DJI Matrice 300 RTK, Skydio X2, Parrot Anafi USA | Infrastructure inspections, utility monitoring, power line surveys | Thermal imaging, zoom capabilities, rugged designs | |
| Photography and Videography Drones | DJI Mavic 3, Sony Airpeak S1, Autel EVO Lite+ | Aerial photography, cinematic videography, real estate marketing | High-resolution cameras, stable gimbals, intelligent flight modes | |
| Public Safety Drones | DJI Matrice 30T, Autel EVO II Dual 640T, Skydio X2 | Emergency response, search and rescue, disaster assessment | Thermal imaging, night vision, long flight times | |
| Racing Drones | DJI FPV, Emax Hawk Pro, iFlight Nazgul Evoque | Competitive drone racing, high-speed flying | Lightweight design, fast maneuvering, customizable | |
| Surveying and Mapping Drones | WingtraOne, DJI Phantom 4 RTK, senseFly eBee X | Topographic mapping, land surveying, environmental monitoring | High-resolution imaging, GPS integration, LIDAR capabilities |
Drone Types with Pictures
Before we get into specifics about each different type of drone, we want to show you what they look like.
Here are the three types of drones we’ll share photos of in this section:
- Drone Types with Pictures—Organized by Rotor Configuration
- Drone Types with Pictures—Organized by Size
- Drone Types with Pictures—Organized by Use Case
Drone Types with Pictures—Organized by Rotor Configuration
Quadcopters Drones (type of multi-rotor)
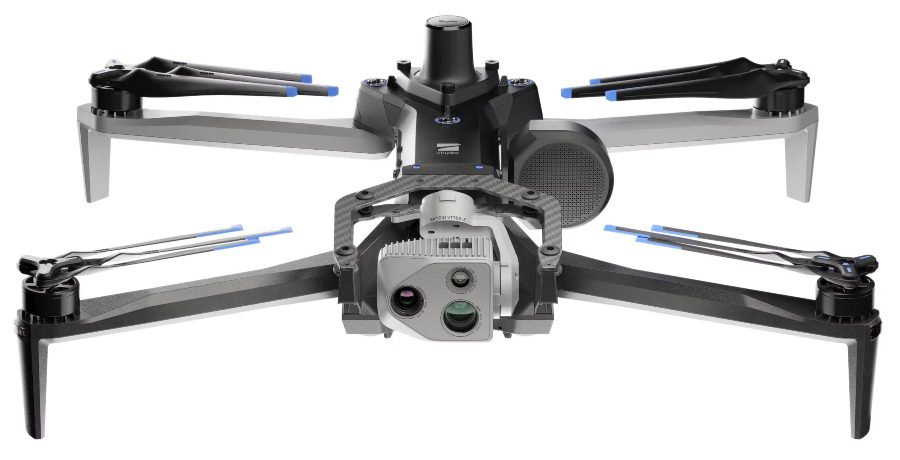

The Skydio X10 Quadcopter Drone
Hexacopter Drones (type of multi-rotor)

The Freefly Alta Hexacopter Drone
Octocopter Drones (type of multi-rotor)
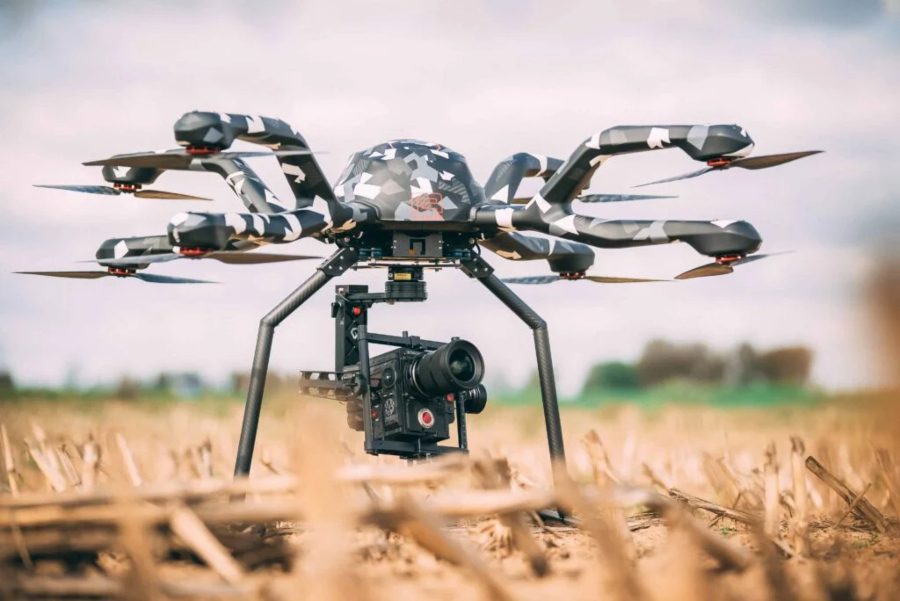

The Acecore Neo Octocopter Drone
Fixed Wing Drones

The eBeeX Fixed Wing Drone
Single-Rotor Helicopter Drones

The Velos Single-Rotor Helicopter Drone
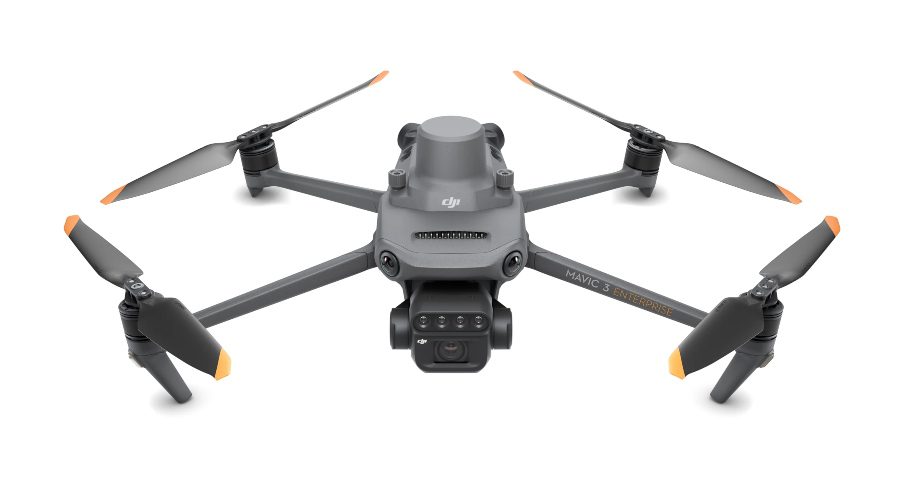
Fixed-Wing Hybrid VTOL Drones

The SkyEye Sierra Fixed-Wing Hybrid VTOL Drone
Drone Types with Pictures—Organized by Size
Nano Drones
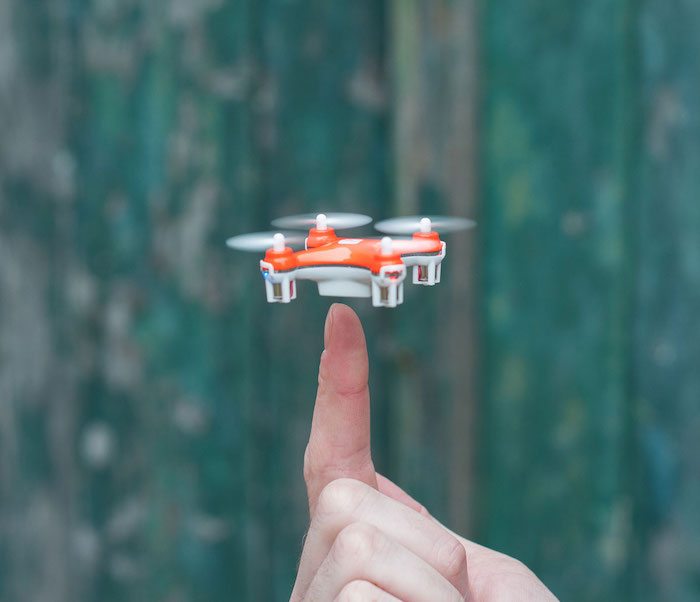

The SkyEye Nano Drone
Small Drones
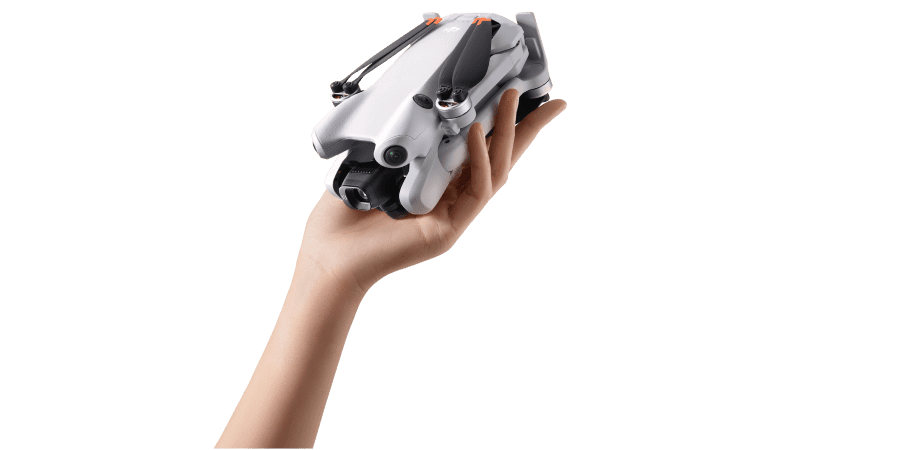

The DJI Mini 4 Pro Small Drone
Medium Drones

The DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise Medium Drone
Large Drones
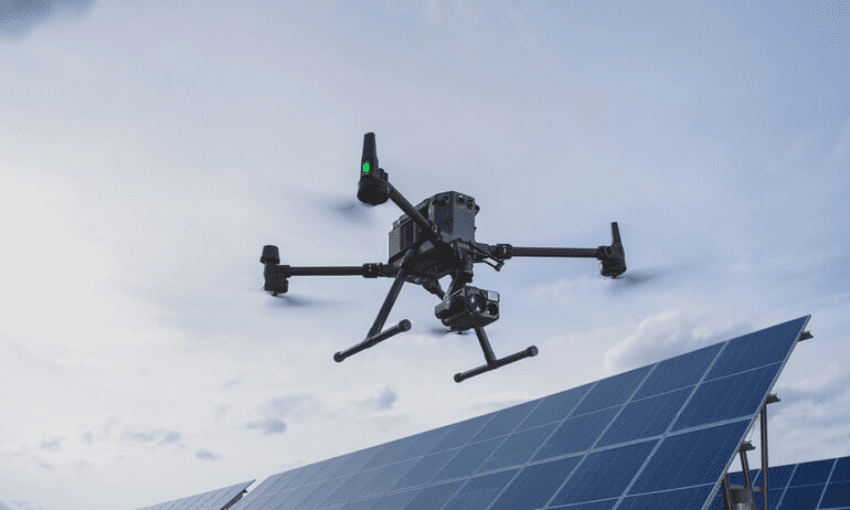

The DJI Matrice 350 RTK Large Drone
Heavy-Lift Drones
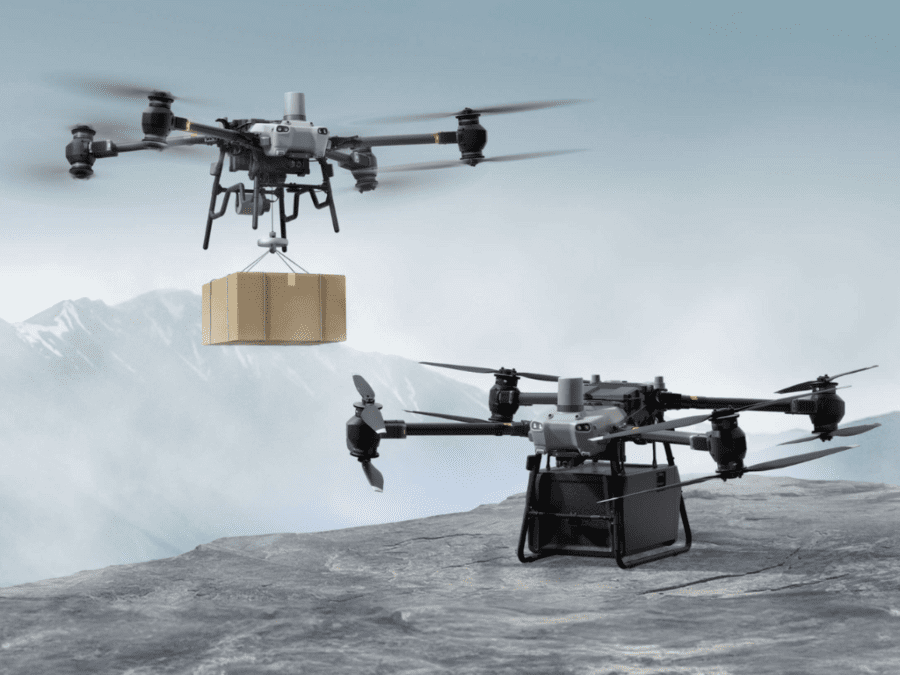
The DJI FlyCart 30 Heavy Lift Drone
Drone Types with Pictures—Organized by Use Case
Agriculture Drones
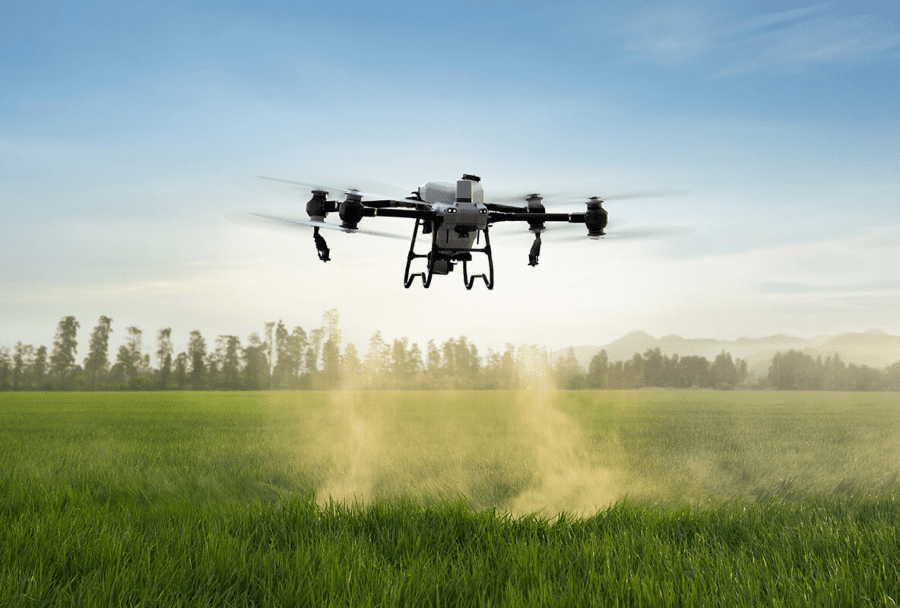

The DJI Agras T50 Agriculture Drone
Delivery Drones
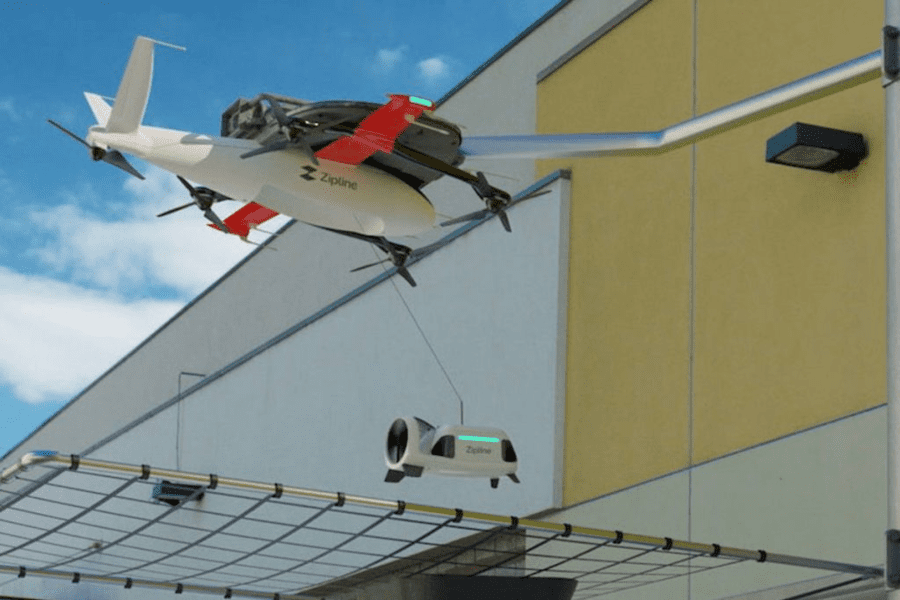
The Zipline Delivery Drone
Inspection Drones

The Voliro T5 inspection drone
Photography and Videography Drones

The Autel Evo Lite+ Photography Drone
Public Safety Drones
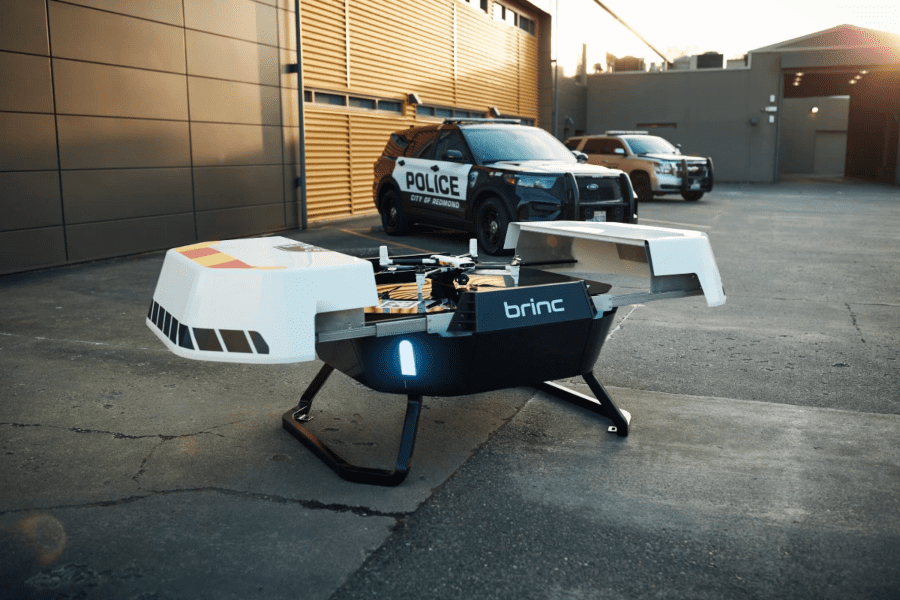

The Brinc Responder Public Safety Drone
Racing Drones
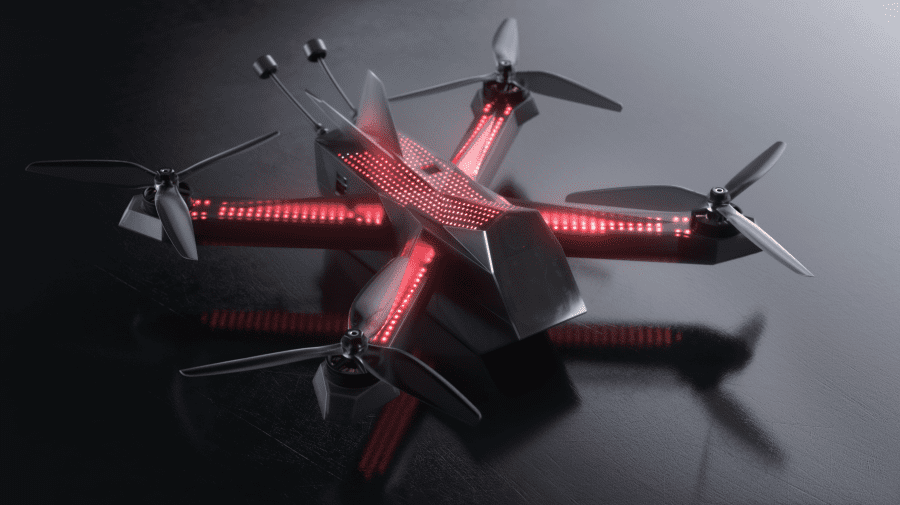
The Drone Racing League Racer 4 Racing Drone
Surveying and Mapping Drones

The WingtraOne Gen II Surveying and Mapping Drone
Drone Type 1: Organized by Rotor Configuration
As we covered above, one of the most common ways to categorize drones is by how many propellers—or rotors—they have, and how those rotors are configured.
A drone’s rotor configuration directly impacts its flight characteristics, stability, and use cases. This table covers the main types of rotor configurations for drones:
| Drone Type | Typical Uses | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Rotor Drones | Photography, inspections, recreational flying | Includes quadcopters, hexacopters, and octocopters; exceptional stability; precise hovering; shorter flight times | $50 – $50,000+ |
| Fixed-Wing Drones | Mapping, surveying, long-range monitoring | Airplane-like design; long flight duration; efficient energy usage; requires runway or catapult for takeoff | $5,000 – $50,000+ |
| Single-Rotor Helicopter Drones | Heavy payload transport, research, military applications | Single large rotor; extended flight times; high payload capacity; more complex to operate | $10,000 – $100,000+ |
| Fixed-Wing Hybrid VTOL Drones | Surveying, mapping, search and rescue | Combines vertical takeoff and landing with efficient forward flight; versatile for diverse environments | $10,000 – $200,000+ |
Multi-Rotor Drones
Multi-rotor drones are the most commonly used type of drone, especially for consumer and professional photography.
These drones use multiple rotors—usually four, six, or eight—to achieve precise hovering, stability, and control. Their ability to remain stationary in mid-air makes them perfect for capturing detailed images or conducting close-range inspections.
- Quadcopters. The most popular type, featuring four rotors. They are versatile and suitable for both beginners and professionals.
- Hexacopters. With six rotors, hexacopters offer enhanced stability and greater payload capacity, ideal for professional photography or inspections.
- Octocopters. Designed with eight rotors, octocopters are used for heavy-duty tasks like carrying cinema-grade cameras or specialized sensors.
| Multi-Rotor Type | Rotor Count | Typical Uses | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quadcopter | 4 rotors | Recreational flying, photography | Most common design; stable and easy to use |
| Hexacopter | 6 rotors | Professional photography, industrial inspections | Greater lift capacity and stability than quadcopters |
| Octocopter | 8 rotors | Heavy-duty tasks, filmmaking | Handles larger payloads; provides redundancy for increased safety |
Fixed-Wing Drones
Fixed-wing drones resemble traditional airplanes with wings that provide lift.
Instead of hovering, these drones glide through the air, making them highly efficient for long-range missions. They are widely used in industries such as mapping, surveying, and environmental monitoring.
- Strengths. Long flight times, energy efficiency, and the ability to cover large areas.
- Limitations. Requires runways or catapults for takeoff and lacks the ability to hover.
Single-Rotor Helicopter Drones
Single-rotor drones operate like traditional helicopters, using one large rotor for lift and a smaller rotor for stability. These drones are known for their high efficiency and payload capacity, making them suitable for specialized tasks such as transporting heavy equipment or conducting research.
- Strengths. High payload capacity, longer flight times, and efficient energy use compared to multi-rotor drones.
- Limitations. More complex to operate and maintain, with higher operational risks.
Fixed-Wing Hybrid VTOL Drones
Hybrid VTOL (Vertical Takeoff and Landing) drones combine the best of both worlds: the long flight capabilities of fixed-wing drones and the vertical takeoff and landing abilities of multi-rotor drones.
These drones are versatile and well-suited for missions in remote or challenging environments.
- Strengths. Can take off and land in confined spaces while offering long-range flight capabilities.
- Limitations. Higher cost and complexity compared to traditional fixed-wing or multi-rotor drones.
Drone Type 2: Organized by Size
The size of a drone plays a major role in determining its functionality, capabilities, and applications.
Drones come in a variety of sizes, from tiny nano drones to large industrial machines, each tailored to meet specific needs. Understanding drone types and sizes helps in selecting the right model based on your goals, whether for recreation, professional tasks, or specialized commercial work.
Here’s an overview:
| Drone Size | Typical Uses | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nano Drones | Indoor flying, casual use, beginner training | Lightweight, simple controls, short flight times (5-10 minutes) | $50 – $200 |
| Small Drones | Photography, travel, recreational flying | Portable, GPS stabilization, cameras up to 4K resolution | $300 – $1,500 |
| Medium Drones | Professional photography, inspections, mapping | Advanced flight modes, obstacle avoidance, 4K or higher cameras | $1,500 – $5,000 |
| Large Drones | Industrial inspections, agriculture, delivery, public safety | High payload capacity, long flight times, rugged design | $5,000 – $50,000+ |
| Heavy-Lift Drones | Carrying heavy payloads for delivery, cinematic equipment for filmmaking | High weight capacity, reinforced frames, advanced stabilization systems | $15,000 – $100,000+ |
Nano Drones: Small Size, Big Potential
Price range: $50 to $200
Nano drones are the smallest drones available, often fitting in the palm of your hand. These drones are lightweight, affordable, and perfect for indoor flying or casual use. While they may lack advanced features, their portability and ease of use make them a fun choice for beginners or hobbyists.
- Key features. Simple controls, short flight times (5-10 minutes), and limited range.
- Best for. Indoor flying, kids, and learning the basics of drone operation.
Small Drones: Compact and Portable
Price range: $300 to $1,500
Small drones are slightly larger than nano drones and often come with more advanced features, such as high-resolution cameras and GPS stabilization. These drones are widely used by hobbyists and beginner professionals for tasks like photography, videography, and recreational flying.
- Key features. Improved flight stability, camera quality (up to 4K), and flight times of 15-30 minutes.
- Best for. Aerial photography, travel, and light recreational use.
Medium Drones: The Balance Between Size and Power
Price range: $1,500 to $5,000
Medium-sized drones strike a balance between portability and capability. These drones are commonly used in professional fields, offering advanced imaging systems, extended flight times, and greater payload capacity.
- Key features. 4K or higher resolution cameras, obstacle avoidance, and 30-45 minutes of flight time.
- Best for. Real estate photography, inspections, and surveying.
Large Drones: Industrial-Grade Performance
Price range: $5,000 to $50,000+
Large drones are designed for heavy-duty tasks in industries like agriculture, construction, and public safety. They can carry specialized equipment such as thermal cameras, LIDAR sensors, or spraying systems and are built to operate in demanding environments.
- Key features. High payload capacity, long flight times (up to several hours), and rugged construction.
- Best for. Industrial inspections, precision agriculture, and search and rescue operations.
Heavy-Lift Drones: Built for Maximum Payloads
Price range: $15,000 to $100,000+
Heavy-lift drones are engineered for transporting substantial payloads and are commonly used in industries such as delivery, filmmaking, and construction. These drones are capable of carrying heavy equipment like cinema-grade cameras, large delivery packages, or specialized tools, making them indispensable for tasks that demand exceptional carrying capacity and stability.
- Key features. High weight capacity, reinforced frames, advanced stabilization systems, and extended flight times.
- Best for. Delivery logistics, professional filmmaking, heavy equipment transport, and aerial construction tasks.
Drone Type 3: Organized by Use Case
From photography and agriculture to delivery and inspections, there are a range of drones out there tailored for specific use cases.
Here’s a chart laying out commercial drone types by use case, listing their typical uses:
| Drone Type | Typical Uses | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture Drones | Crop monitoring, soil analysis, pesticide spraying | Multispectral sensors, spraying systems, precision mapping | $3,000 – $20,000 |
| Delivery Drones | Medical supply transport, retail and e-commerce logistics | Secure payload systems, autonomous navigation, long-range flight | $5,000 – $40,000 |
| Inspection Drones | Infrastructure inspections, utility monitoring, power line surveys | Thermal imaging, zoom capabilities, rugged designs | $3,000 – $50,000+ |
| Photography and Videography Drones | Aerial photography, cinematic videography, real estate marketing | High-resolution cameras, stable gimbals, intelligent flight modes | $500 – $10,000 |
| Public Safety Drones | Emergency response, search and rescue, disaster assessment | Thermal imaging, night vision, long flight times | $5,000 – $50,000+ |
| Racing Drones | Competitive drone racing, high-speed flying | Lightweight design, fast maneuvering, customizable components | $200 – $2,000 |
| Surveying and Mapping Drones | Topographic mapping, land surveying, environmental monitoring | High-resolution imaging, GPS integration, LIDAR capabilities | $5,000 – $25,000+ |
Now, let’s take a closer look at each of these use cases.
Agriculture Drones: Precision Farming Tools
Agriculture drones are used to enhance productivity and monitor crop health with tools like multispectral sensors and spraying systems. These drones help farmers collect data quickly, identify issues, and optimize their yields.
- Best for. Crop health monitoring, soil analysis, and pesticide application.
- Example drones. DJI Agras T40, senseFly eBee Ag, Parrot Bluegrass
Delivery Drones: Revolutionizing Logistics
Delivery drones are engineered to transport goods efficiently, often equipped with secure payload mechanisms and long-range capabilities. They are becoming increasingly common in industries like healthcare, retail, and food delivery.
- Best for. Medical supply delivery, e-commerce logistics, and food distribution.
- Example drones. Wing Delivery Drones, UPS Flight Forward, Amazon Prime Air
Inspection Drones for Industrial Applications
Inspection drones are essential for industries like construction, oil and gas, and utilities, where close-up inspections of hard-to-reach areas are required. These drones often feature thermal cameras, zoom capabilities, and rugged designs to operate in challenging environments.
- Best for. Infrastructure inspections, power line monitoring, and pipeline surveys.
- Example drones. DJI Matrice 350 RTK, Parrot Anafi USA, Skydio X2
Photography and Videography Drones
Designed for capturing stunning visuals, photography and videography drones are among the most popular types on the market. These drones come equipped with high-resolution cameras, stable gimbals, and intelligent flight modes to ensure smooth and professional-grade footage.
- Best for. Real estate photography, cinematic filmmaking, and social media content creation.
- Example drones. DJI Mavic 3, Autel EVO Lite+
Public Safety Drones
Public safety drones are vital tools for emergency response, disaster assessment, and search and rescue operations. These drones are equipped with specialized features such as thermal imaging cameras, night vision, and loudspeakers to assist in locating missing persons, assessing hazardous areas, or providing critical communication in emergencies. Their ability to operate in challenging conditions makes them indispensable for first responders and public safety agencies.
- Best for. Emergency response, search and rescue missions, disaster assessment, and public safety surveillance.
- Example drones. DJI Matrice 30T, Autel EVO II Dual 640T, Skydio X2
Racing Drones
Racing drones are built for speed, agility, and precision, making them ideal for competitive drone racing and high-speed aerial maneuvers. These drones are lightweight, customizable, and designed for quick acceleration and sharp turns. Pilots typically use first-person view (FPV) goggles to navigate through obstacle courses in real time, providing an immersive racing experience.
- Best for. Competitive drone racing, high-speed flying, and aerial tricks.
- Example drones. DJI FPV, Emax Hawk Pro, iFlight Nazgul Evoque
Surveying and Mapping Drones
Surveying and mapping drones are engineered for precision and efficiency, enabling professionals to collect accurate geospatial data over large areas. These drones often feature advanced sensors, such as LIDAR or high-resolution cameras, and are integrated with GPS systems for precise mapping. Their long flight times and ability to cover vast distances make them ideal for land development, construction, and environmental monitoring.
- Best for. Topographic mapping, land surveying, construction site analysis, and environmental monitoring.
- Example drones. WingtraOne, DJI Phantom 4 RTK, senseFly eBee X
New Drone Types—Emerging Drone Technologies
The drone industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies pushing the boundaries of what drones can do. From artificial intelligence to modular designs, these advancements are transforming traditional drone capabilities, opening doors to new applications and increasing efficiency in existing ones.
In this section, we’ll look at the latest innovations redefining drone technology and their potential impact across industries.
AI-Powered Drones: Smarter Flight
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing drone operations by enabling smarter flight patterns, enhanced object recognition, and autonomous decision-making. AI-powered drones can adapt to their environment in real time, making them highly effective for complex tasks like inspections, search and rescue, and mapping.
- Key features. Real-time object detection, route optimization, and autonomous obstacle avoidance.
- Best for. Industrial inspections, disaster response, and precision agriculture.
- Example drones. Skydio 2+, DJI Matrice 300 RTK with Zenmuse L1.
Autonomous Drones: The Future of Drone Operations
Autonomous drones take automation to the next level, performing missions without human intervention. These drones are equipped with advanced sensors, GPS, and software that enable them to execute pre-programmed tasks like inspections, deliveries, or surveillance with minimal oversight.
- Key features. Fully automated deployment, return-to-home functionality, and data integration with cloud systems.
- Best for. Automated delivery, perimeter security, and environmental monitoring.
- Example drones. Percepto AIM, Skydio Dock, Flytrex Delivery Drones.
Drone-in-a-Box Systems: Autonomous Solutions for Continuous Operations
Drone-in-a-box systems are advanced autonomous solutions that operate without human intervention. These drones are housed in self-contained units that handle charging, data transfer, and deployment, making them ideal for missions requiring ongoing monitoring and rapid response capabilities. By automating routine operations, these systems offer unparalleled efficiency and reliability.
- Key features. Fully autonomous deployment, integrated charging and data transfer, and seamless software integration for remote management.
- Best for. Automated inspections, perimeter security, and long-term industrial monitoring.
- Example drones. Skydio Dock, DJI Dock with Matrice 30, Percepto AIM.
Modular Drones: Customization and Flexibility
Modular drones are designed with interchangeable components, allowing users to customize their drones for specific tasks. Whether swapping out cameras, sensors, or payloads, these drones offer unparalleled versatility, making them a cost-effective solution for multi-use scenarios.
- Key features. Interchangeable payloads, scalable designs, and upgradeable systems.
- Best for. Multi-role applications like inspections, mapping, and agriculture.
- Example drones. Quantum Systems Vector, DJI Matrice 600 Pro, WingtraOne.
Swarm Technology: Coordinated Drones in Action
Swarm technology involves multiple drones working together as a coordinated unit. This innovation has significant potential in areas like large-scale mapping, search and rescue, and military operations, where collaboration among drones can increase efficiency and effectiveness.
- Key features. Synchronized flight, real-time communication, and shared data processing.
- Best for. Large-area surveys, disaster recovery, and tactical military missions.
- Example drones. DARPA Gremlins Program, Parrot ANAFI Ai Swarm Integration.
Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) Operations
BVLOS technology allows drones to operate beyond the operator’s line of sight, a critical advancement for expanding drone applications in industries like delivery, inspections, and agriculture. With regulatory approvals, BVLOS drones are becoming a game-changer for long-distance and large-scale missions.
- Key features. Long-range connectivity, real-time video transmission, and enhanced situational awareness.
- Best for. Delivery services, pipeline inspections, and precision farming.
- Example drones. DJI Matrice 30, Flytrex BVLOS Delivery Drones.
Drone Types FAQ
What are the main types of drones?
The main types of drones include fixed-wing drones, multirotor drones, and hybrid drones. They can also be categorized by their applications, such as photography drones, agriculture drones, racing drones, and industrial inspection drones.
What is the difference between fixed-wing and multirotor drones?
Fixed-wing drones are designed like airplanes and are ideal for long-distance flights and large-area surveys, as they are more energy-efficient. Multirotor drones, on the other hand, can hover in place and are better suited for photography, inspections, and tasks requiring precision maneuvering.
Which drone type is best for photography?
Multirotor drones are the best choice for photography and videography due to their ability to hover, capture stable shots, and maneuver precisely. Popular models include the DJI Mavic 3 and Sony Airpeak S1.
How are drones categorized by size?
Drones are often classified as nano, small, medium, or large based on their size and capabilities. Nano and small drones are portable and easy to use, while medium and large drones are more robust and often used for professional or industrial purposes.
What are industrial drones used for?
Industrial drones are used for tasks like infrastructure inspections, surveying, agricultural monitoring, and environmental data collection. They are equipped with specialized tools such as thermal cameras, LIDAR, or multispectral sensors.
Can drones be used underwater?
Yes, underwater drones, also known as ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles), are designed specifically for underwater exploration, inspections, and filming. Examples include the Chasing M2 and Blueye Pioneer.
What is the typical price range for drones?
Drones range widely in price depending on their type and purpose. Consumer drones can cost between $50 and $1,500, professional drones range from $1,500 to $50,000, and specialized drones can exceed $100,000.
How do I choose the right drone type for my needs?
Choosing the right drone depends on your intended use, budget, and required features. For example, photography enthusiasts should prioritize drones with high-resolution cameras, while industrial users might need drones with advanced sensors or payload capacity.
